
This part must play the roles of Account Service client and accounts payable server. It transforms accounts payable requests into CORBA method invocations and uses the method results to send an accounts payable reply. This part is called the client wrapper.
Figure 1. System Context - Client Wrapper
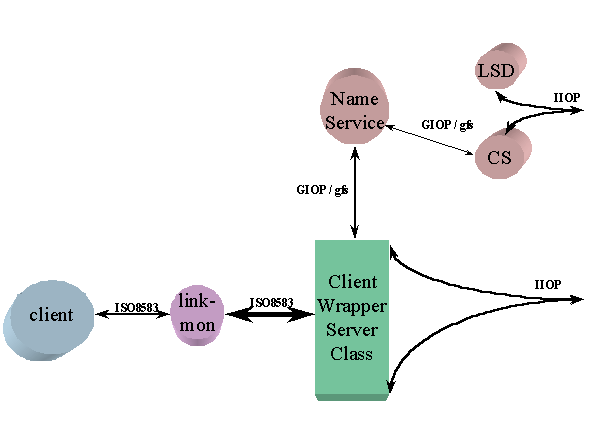
The server asks the Naming Service to bind the Account_Service name to its factory reference. Because the Naming Service is configured to use_comm_server, the IIOP profile in its IOR will contain the LSDís address, allowing it to pick the best CS for subsequent traffic to the services. Note that in this version of NonStop DOM 2.0, this feature adds no value.
This client wrapper runs as a NonStop TS/MP server class. The processes are configured to use the Guardian file system and TCP client protocols.
The client wrapper processes use the NonStop DOM Naming Service to resolve the name Account_Service to the serverís Factory reference. Each then narrows the result to Account_Service::Factory and invokes the Create method. They then wait for accounts payable requests, and perform the corresponding Inquiry, Credit, and Debit methods against their Account_Service::Account reference.
The accounts payable client communicates with the client wrapper via NonStop TS/MP as it would with an accounts payable server.
Figure 2. Internal Process Architecture of Client Wrapper
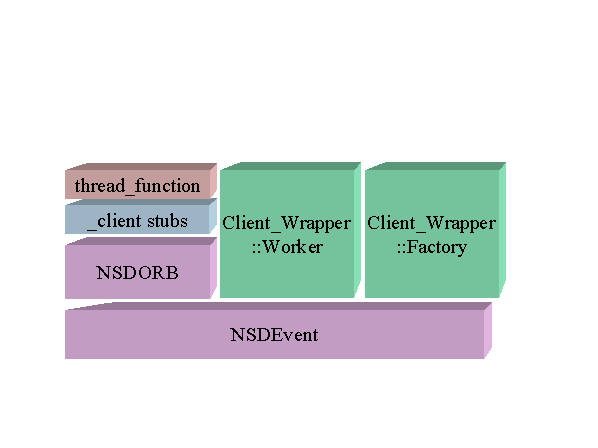
The internal architecture of the client wrapper is a mixture of a Guardian File System (GFS) server and CORBA client. The Factory uses NSDEvent parts to wait for OPEN messages on $receive (from the LINKMON process). When it receives an OPEN, the Factory creates a Worker to service that GFS connection.
The Worker uses NSDEvent parts to wait for WRITEREAD and CLOSE messages from LINKMON. When a WRITEREAD event is received, the Worker launches a thread, passing the event as an argument, detaches the thread (indicating it is not interested in a subsequent join) then returns. This means that for each WRITEREAD event that is received, a thread is launched to process it to completion.
The threads in a client wrapper process share a single process. The first thread to execute uses the NSDORB parts to ask the Naming Service to resolve the server name to a Factory reference, then uses it to create an account reference.
A thread then interprets the Fw_MD of the event as an ISO8583 request message and invokes the corresponding method on the Account reference. The method results are used to generate an IS8583 response message. That response is written into the event Fw_MD, and the eventís reply method is invoked. That is the end of the threadís work, so the thread_function completes.
Figure 3. Class Description

The Client_Wrapper::Factory is a Guardian File System listener event handler user (NSDEFw_GFS::Listener_EH_User). It constructs a listener event handler for the null subdevice (that is, LINKMON opens the process). When OPEN messages arrive on $RECEIVE, the event handler will invoke the connect_in method. The Worker destructor calls signal.
The Client_Wrapper::Worker is an NSDEFw_GFS::Server_Event_Handler. It is created by the Factory to serve a File System connection. The cv_worker count is bumped by the constructor, then dropped and checked by the destructor. A worker registers itself with the NSDEFw_Receive_Handler as interested WRITEREAD and CLOSE events for its connection. For each WRITEREAD event, a Worker launches a thread_function, which uses transformation functions and the Account_Service::Account_client stubs. Receipt of a CLOSE event causes the Worker to self-destruct.
The client wrapper main function initializes the ORB, creates a Client_Wrapper::Factory, then calls the factory wait method. When the last CLOSE message is received from LINKMON, the wait method completes, and the process terminates.
The wait method simply waits on its condition variable.
The connect_in method creates an instance of Worker and tells it to accept the connection.
The accept method uses the key parameter to register interest in I/O and close events with the Receive_Handler.
The handle_event method is called from the Receive_Handler, itself a GFS Client event handler relative to $RECEIVE. The Worker decides to call the handle_writeread or handle_close implementation.
The handle_writeread method is called from handle_event. It launches a thread_function to process the writeread, then sets the thread free with Fw_Thread::detach.
The handle_close method is called from handle_event. It calls delete this.
The find_server method is called from the thread_function. It use the Naming Service to resolve the name Account_Service. The result is narrowed to Account_Service::Account and placed in cp_account.
The thread function is launched by the handle_writeread implementation. It performs the following:
find_server if necessaryAccount_Service method